Spatial Maps in Voting Advice Applications: The Case for Dynamic Scale Validation
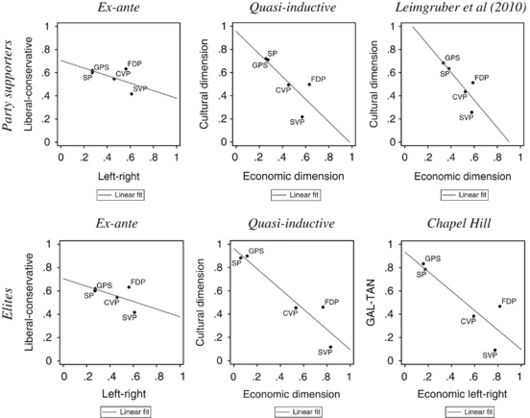 Comparing ex-ante defined ideological positions with dynamically validated positions (quasi-inductive) and two `gold standards’ (Switzerland, 2007)
Comparing ex-ante defined ideological positions with dynamically validated positions (quasi-inductive) and two `gold standards’ (Switzerland, 2007)
Abstract
Low-dimensional spatial representations of political preferences are a widespread feature of voting advice applications (VAAs). Currently, VAA spatial maps tend to be defined on the basis of a priori reasoning. This article argues that VAA spatial maps should be empirically validated to safeguard fundamental psychometric properties – in particular, unidimensionality and reliability. We suggest dynamic scale validation as a pragmatic method for improving measurement quality in VAA spatial maps. The basic logic of dynamic scale validation is to exploit early user data as a benchmark against which ex-ante defined maps can be evaluated. We draw on data from one of the most institutionalised VAA settings, Switzerland, to illustrate this dynamic approach to scale validation.