Getting out the Vote with Voting Advice Applications
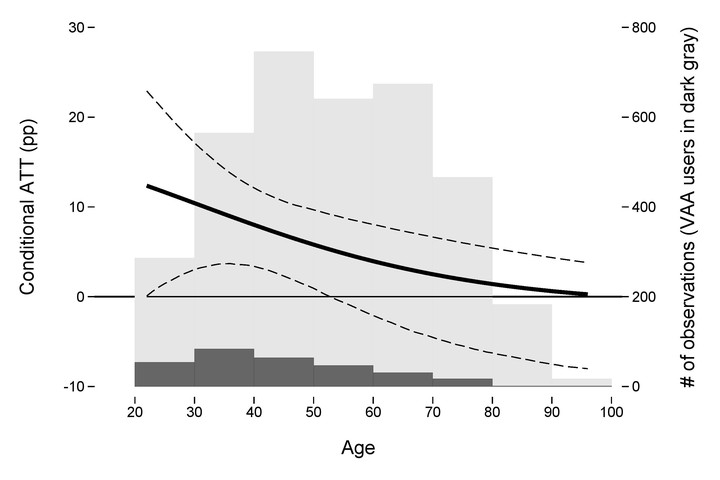 Effect of smartvote usage on individual-level turnout probabilities conditional on age
Effect of smartvote usage on individual-level turnout probabilities conditional on age
Abstract
This article investigates the mobilization potential of online voter information tools known as “Voting Advice Applications” (VAAs). We argue that an observational approach utilizing survey data constitutes the best available method for causal inference where VAAs are popular—and we are thus most interested in VAA turnout effects—because randomized experiments are likely to run into double cross-over problems. We suggest that matching offers key improvements over existing methods to tackle self-selection into VAA use in observational studies. To improve confidence in selection on observables, we complement matching estimates with an extensive sensitivity analysis, including a placebo test. Empirically, we study the effect of smartvote, a popular VAA from Switzerland, on turnout in the 2007 Swiss federal election. We find that smartvote usage significantly increased the individual-level probability to vote. Our results suggest that smartvote was, on the aggregate, responsible for about 1.2 % points of the total tally with an estimated cost of nine Swiss Francs (7.5 U.S. dollars or 1.4 `Big Macs’) per additional vote. Promising as well, we find that the mobilization effect was more pronounced among younger voters. Our findings point to the value of VAAs compared to traditional get out the vote tactics.